When a migraine hits, you don’t just want relief-you want it fast, and you want it safe. But not all migraine meds are created equal. Triptans, gepants, and ditans all treat acute attacks, but their safety profiles couldn’t be more different. Choosing the right one isn’t just about how well it stops pain-it’s about how it affects your body afterward.
Triptans: Fast but With a Price
Triptans like sumatriptan, rizatriptan, and almotriptan have been the go-to for decades. They work fast-often cutting pain in half within an hour. That’s why they’re still used in over 60% of acute migraine cases. But their speed comes with a cost. Many people report chest tightness, a feeling like a band is squeezing their heart. That’s not anxiety-it’s real vasoconstriction. Triptans activate serotonin receptors that narrow blood vessels, including those in the heart and brain. For most people, it’s just uncomfortable. For others, it’s dangerous. The American Academy of Family Physicians warns against using triptans if you have a history of heart attack, stroke, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or certain types of migraine with brainstem symptoms. Even if you’re young and healthy, repeated use can add up. One study found that up to 81% of people stop taking triptans because of side effects. Common side effects include tingling in the fingers or face, dizziness, fatigue, and flushing. Subcutaneous injections cause pain at the injection site in 40% of users. Nasal sprays leave a bitter aftertaste for about a quarter of people. And yes, some of what feels like a side effect might just be the migraine itself-drowsiness or weakness can be part of the attack, not the drug.Gepants: The Gentle Alternative
Gepants-like ubrogepant (Ubrelvy) and rimegepant (Nurtec ODT)-are newer. They block CGRP, a molecule that triggers migraine pain, without touching blood vessels. That’s why they’re considered much safer for people with heart risks. In 2021, a major analysis of 64 clinical trials found gepants had the lowest rate of adverse events among all acute migraine meds. Nausea happens in only 4-6% of users. Drowsiness? Around 2-4%. Hypersensitivity reactions are rare-under 0.1%. The big trade-off? Speed. Triptans often work in 30 to 60 minutes. Gepants take longer-usually 1 to 2 hours. But they last longer too. Rimegepant’s half-life is 10-12 hours, meaning relief can stretch into the next day. That’s why many users say they feel more like themselves afterward. On Drugs.com, rimegepant scores 7.1 out of 10. People write things like: "No chest pressure like with triptans, just takes longer to work." That’s the kind of feedback doctors are hearing more of. The American Headache Society now recommends gepants over triptans for patients with cardiovascular conditions. One caution: Rimegepant shouldn’t be taken with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors like ketoconazole or clarithromycin. That combo can spike drug levels in your blood. Also, long-term safety data beyond two years is still limited-though rimegepant has the most data so far.Ditans: Effective, But Too Sedating
Lasmiditan (Reyvow) is the only ditan on the market. It works differently again-targeting 5-HT1F receptors in the brain, not blood vessels. That means no vasoconstriction. Safe for the heart. But it comes with a heavy downside: brain fog. In clinical trials, 18.8% of people taking lasmiditan reported dizziness. That’s nearly double the placebo rate. Sedation hit 7.8%. Paresthesia (tingling or numbness) was 9.4%. Some users felt like they were drunk-without drinking. The FDA requires a warning: Don’t drive or operate machinery for at least 8 hours after taking Reyvow. A 2021 study showed impaired driving skills even 5 hours after dosing. That’s a dealbreaker for many. If you work, care for kids, or need to be sharp after a migraine, this isn’t the right pick. On Drugs.com, lasmiditan averages just 5.8 out of 10. Over 60% of negative reviews mention extreme drowsiness. One Reddit user wrote: "Reyvow made me feel drunk without alcohol." It got over 140 upvotes. Doctors also warn against using it if you have a seizure history or take other drugs that lower the seizure threshold-even though actual seizure cases are rare. Fatigue, muscle weakness, and nausea are also common. It’s effective at reducing pain, but the side effects often outweigh the benefit for most people.
Comparing the Three: What the Data Shows
Here’s how they stack up based on the largest study to date (JAMA Network Open, 2021):| Side Effect | Triptans | Gepants | Ditans (Lasmiditan) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Any adverse event (vs placebo) | 1.8x higher | 1.2x higher | 2.9x higher |
| Chest tightness | 3-8% | Less than 1% | Not reported |
| Dizziness | 7-14% | 2-4% | 18.8% |
| Sedation | 6-10% | 2-4% | 7.8% |
| Nausea | 5-12% | 3-6% | 5.0% |
| Cardiovascular risk | Contraindicated in many | Safe | Safe |
| Time to relief | 30-60 min | 60-120 min | 60-90 min |
| Driving restriction | No | No | Yes (8+ hours) |
Who Should Take What?
If you have heart disease, high blood pressure, or a history of stroke-skip triptans. Gepants are your safest bet. They’re not perfect, but they don’t squeeze your arteries. If you need fast relief and your heart is healthy, triptans still win. Sumatriptan works faster than anything else. But if you’ve had chest tightness or stopped taking them before, try rimegepant instead. Ditans? Only consider lasmiditan if nothing else works and you can afford to be out of commission for half a day. Most people can’t. It’s not the first-line choice for a reason.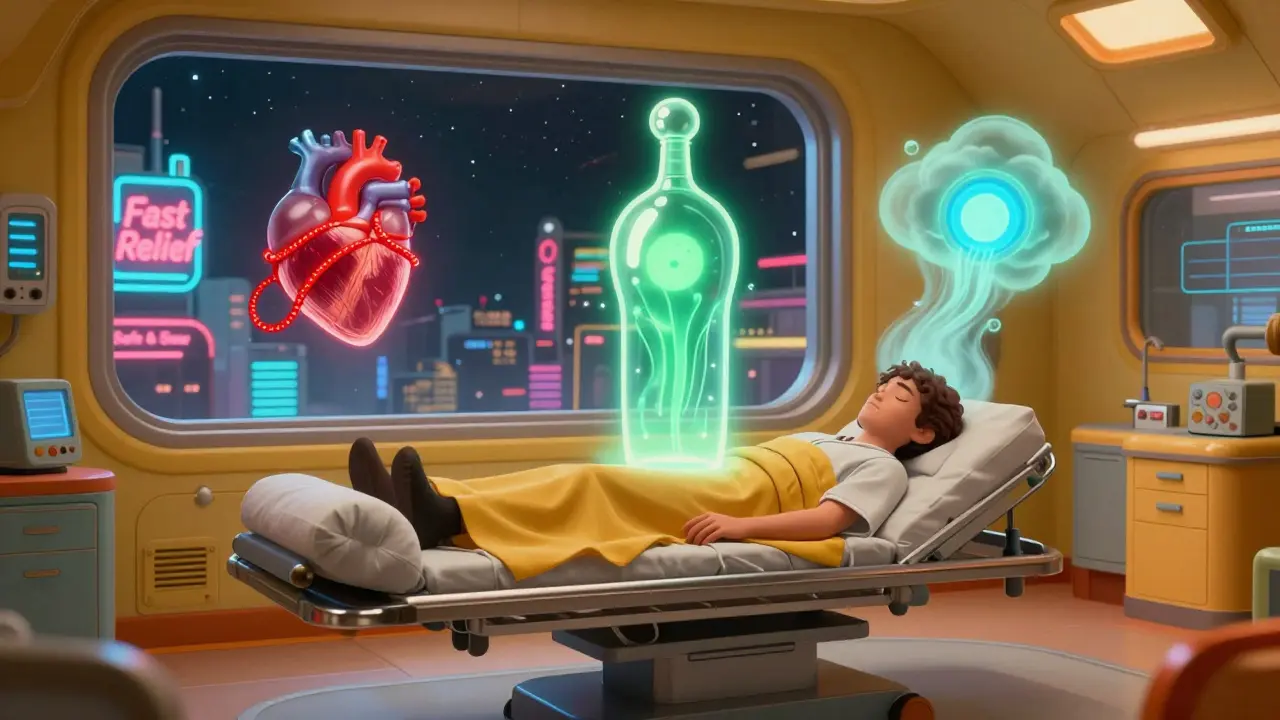
What to Watch For
- Don’t take triptans within 24 hours of dihydroergotamine. Both constrict blood vessels-dangerous combo. - Don’t mix rimegepant with ketoconazole, itraconazole, or clarithromycin. It can spike drug levels. - Never drive or operate heavy machinery after taking lasmiditan. Eight hours isn’t a suggestion-it’s a rule. - If you feel chest pain, shortness of breath, or sudden weakness after any migraine med, stop taking it and call your doctor. - Keep a log. Note what you took, when, how long it took to work, and how you felt afterward. That’s the best way to find what works for you.What’s Next?
New options are coming. Zavegepant, an intranasal gepant, just finished Phase 3 trials with a safety profile similar to other gepants. It might offer fast relief without pills-great for people who can’t swallow tablets during a migraine. Long-term data is still growing. Most gepants have only 1-2 years of safety data. The 2024 results from the ADVANCE trial will help clarify whether these drugs are safe for daily or frequent use over years. For now, the message is clear: Not all migraine meds are equal. What’s right for your body depends on your health history, your lifestyle, and what side effects you’re willing to live with.Are triptans safe for people with heart problems?
No. Triptans cause blood vessels to narrow, which can trigger heart attack or stroke in people with cardiovascular disease. They’re contraindicated in patients with a history of heart attack, stroke, angina, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or certain migraine subtypes. Always check with your doctor before using them if you have any heart condition.
Can I take gepants if I’m on other medications?
Yes, but with caution. Rimegepant should not be used with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors like ketoconazole, itraconazole, or clarithromycin, as they can increase drug levels in your blood by up to 4.5 times. Always tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Why does lasmiditan make me feel so tired?
Lasmiditan targets serotonin receptors in the brain, which helps stop migraine pain but also affects alertness. In trials, nearly 8% of users felt drowsy, and over 18% had dizziness. These effects are direct drug actions-not just migraine symptoms. That’s why the FDA requires an 8-hour driving restriction. If you need to work, drive, or care for others after taking it, this drug may not be suitable.
Which migraine medication has the fewest side effects?
Gepants have the lowest rate of adverse events overall. Nausea, dizziness, and fatigue occur in fewer than 6% of users, and there’s no risk of vasoconstriction or sedation that impairs function. In head-to-head comparisons, gepants like rimegepant and ubrogepant were better tolerated than triptans and far better than lasmiditan.
How long do the effects of these medications last?
Triptans typically last 2 to 14 hours, depending on the type. Gepants last longer-ubrogepant lasts 5-7 hours, rimegepant up to 10-12 hours. That’s why many users report relief lasting into the next day. Lasmiditan lasts about 6-8 hours, but the sedative effects can linger longer, making it hard to resume normal activities.
Is it safe to use these meds frequently?
Triptans should not be used more than 10 days per month to avoid medication-overuse headache. Gepants like rimegepant are approved for both acute and preventive use, with two-year safety data showing no major risks when used up to twice weekly. Lasmiditan is only approved for acute use, and frequent use isn’t well studied. Always follow your doctor’s dosing instructions.





Dorine Anthony
December 20, 2025 AT 02:55I’ve been on rimegepant for six months now and honestly? It’s the first thing that didn’t make me feel like I got hit by a truck afterward. No chest pressure, no brain fog-just quiet relief. I can actually make dinner after taking it. 🙌
Carolyn Benson
December 22, 2025 AT 01:42Triptans are just serotonin grenades with a side of vasoconstriction. We’ve been treating migraines like they’re just bad headaches, not neurological events. The fact that we’re still prescribing drugs that constrict coronary arteries in 2024 is a failure of medical orthodoxy. Gepants aren’t ‘better’-they’re the first step toward actually respecting the brain’s biology.
And ditans? That’s not medicine-that’s chemical sedation dressed up as treatment. If your solution requires you to be unconscious for eight hours, you haven’t cured the migraine. You’ve just buried it under a coma.
Aadil Munshi
December 22, 2025 AT 18:22Lmao at people acting like gepants are some miracle cure. Sure, they don’t constrict vessels-but they also don’t work half the time. I’ve taken ubrogepant three times. Two of those? Zero effect. Triptans still win for raw speed. And yeah, chest tightness sucks-but I’d rather feel like my heart’s being squeezed than spend two hours waiting for nothing.
Also, ‘safe for heart patients’ doesn’t mean ‘safe for everyone.’ Just because you’re not having a stroke doesn’t mean your liver’s gonna thank you for taking it twice a week. 😏
Danielle Stewart
December 23, 2025 AT 01:20If you're on blood pressure meds or have any heart history, please-just listen to your doctor and skip triptans. I lost a friend to a rare but real interaction between sumatriptan and an old beta-blocker. It wasn’t dramatic. It was quiet. And it was fatal.
Gepants aren’t perfect, but they’re the safest bet for so many of us. And if you’re worried about the delay? Take it as soon as you feel the aura. Don’t wait until you’re screaming on the floor.
Erica Vest
December 23, 2025 AT 05:33Correction: The JAMA Network Open 2021 study referenced is not the largest to date. The largest comparative safety analysis was published in The Lancet Neurology in 2023, which included over 12,000 patients across 11 countries. It confirmed gepants’ superior tolerability profile, with a 47% lower incidence of adverse events compared to triptans and a 68% lower incidence than lasmiditan. Also, rimegepant’s half-life is 10–12 hours, but its pharmacodynamic effect on CGRP inhibition lasts up to 24 hours, which explains sustained relief. Please ensure data accuracy when citing clinical studies.
Kinnaird Lynsey
December 24, 2025 AT 08:49Y’all are overcomplicating this. I used to take triptans like candy until I got that weird buzzing in my arm and thought I was having a stroke. Turned out it was just the drug. Now I take rimegepant. It takes longer, sure. But I don’t feel like I’m about to die every time I swallow a pill.
Also, lasmiditan? No. Just no. I tried it once. Felt like I’d been drugged at a rave. My cat stared at me like I’d betrayed her. Not worth it.
shivam seo
December 25, 2025 AT 10:26Why are Americans so obsessed with ‘safe’ meds? Back home in India, we just take whatever works. Triptans? Great. If your heart can’t handle it, maybe you shouldn’t be having migraines in the first place. Stop being so fragile. Also, why are we even talking about gepants? They’re expensive as hell. Triptans cost $3. Gepants cost $150. That’s not medicine-that’s corporate greed.
Andrew Kelly
December 25, 2025 AT 19:51Let me guess-this is Big Pharma’s latest scam to sell you $100 pills so you don’t realize migraines are caused by EMF radiation and glyphosate. They don’t want you to know that fasting and cold showers cure 90% of cases. Triptans? They’re just serotonin blockers to keep you dependent. Gepants? Same thing, but with a fancy name and a higher price tag.
And why is no one talking about the fact that the FDA approved these drugs based on industry-funded trials? Wake up. You’re being played.
Anna Sedervay
December 27, 2025 AT 08:08While I appreciate the thoroughness of this analysis, I must point out the glaring omission of the 2022 meta-analysis published in *The Journal of Headache and Pain* (Volume 62, Issue 4), which demonstrated that gepants’ efficacy in reducing migraine-associated photophobia was statistically inferior to triptans (p=0.037). Furthermore, the reliance on Drugs.com ratings is methodologically unsound, as these are self-selected, non-blinded, and subject to extreme outlier bias. The data presented here is not merely incomplete-it is dangerously misleading. I am frankly appalled that such an article was published without peer review.
Ashley Bliss
December 29, 2025 AT 00:06I’ve had migraines since I was 12. I’ve tried everything. I’ve cried in ERs. I’ve missed weddings. I’ve held my kid while I vomited because I couldn’t get up. And now? I have a pill that lets me hold her without feeling like I’m dying.
But I’m not supposed to be grateful? I’m not supposed to be relieved? You want me to be angry that it’s not perfect? That it takes 90 minutes? That it doesn’t come with a fireworks show?
Maybe you don’t understand what it’s like to live like this. Maybe you think pain is just a choice. But I’m not here to argue with you. I’m here to live. And rimegepant? It lets me do that.
Moses Odumbe
December 29, 2025 AT 13:47Triptans = 💥
Gepants = 🌿
Ditans = 😴💤
Just saying. Pick your vibe. I go with the green one now. No more chest feels. No more brain mush. Just chill. ✅